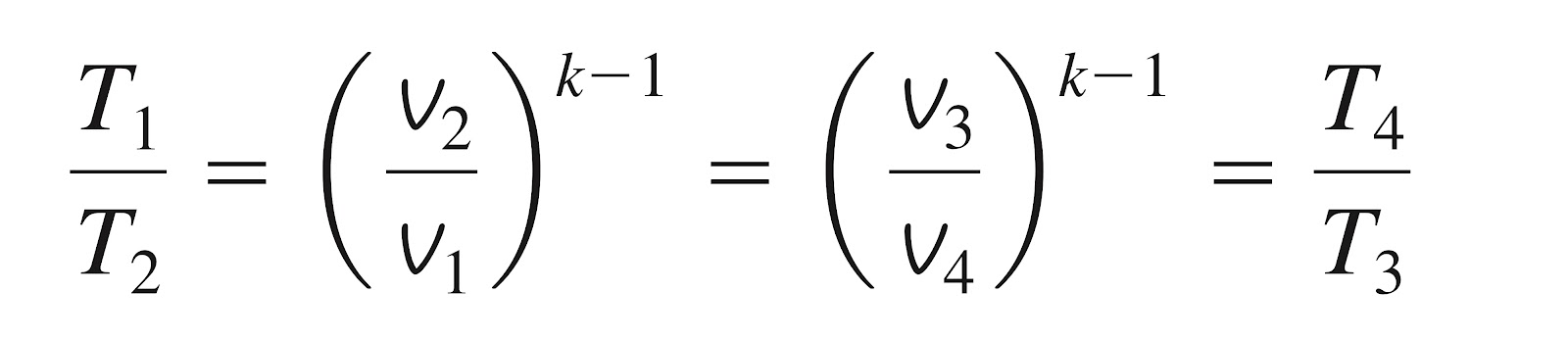Kumpulan catatan selama berkativitas terutama pembangkit listrik, energi dan lainnya
Tuesday, February 13, 2024
Sunday, February 11, 2024
Siklus Otto, Aktual dan Ideal (1)
 |
| Sumber : Museum Angkut Malang (7 feb 24) |
Siklus otto merupakan siklus ideal untuk jenis mesi n recripocating dengan penyalaan dengan spark atau spark ignition. Siklus ini bisa dijelaskan dengan diagram dari masing-masing kondisi sebagai yang dijelaskan dalam diagram p-v sebagai berikut;
Saturday, October 28, 2023
Prinsip Kerja Mesin Diesel
Diesel merupakan salah satu mesin konvensi energi yang terjadi secara internal combustion dengan fluida kerja berupa udara yang tidak mengalami perubahan fasa saat proses masuk, terjadinya pembakaran hingga keluar sebagai udara buang melalui cerobong exhaust. Merangkum dari buku Thermodynamic karangan Yunus Cengel yang sering jadi acuan beberapa mata kuliah (bab 9 halaman 488).
Salah satu jenis konversi energi dalam mesin pembakaran berjenis reciprocating atau bersifat bolak balik memiliki prinsip kerja ketika bahan bakar diumpankan kedalam ruang bakar dan tercampur dengan udara kemudian terkompresi energi (kimia) menjadi panas yang dapat menggerakkan secara mekanis suatu piston. Perubahan energi kimia (pembakaran) menjadi energi kinetik inilah yang dimanfaatkan untuk konversi energi yang dapat dimanfaatkan dalam proses berikutnya, apakah itu menjadi putaran roda ataupun menjadi penggerak generator untuk menghasilkan energi listrik.
Mesin diesel adalah salah satu jenis mesin konversi energi dengan prinsip recripocating secara pembakaran internal. Sedangkan fluida kerjanya adalah udara yang tidak mengalami peubahan fasa dan hanya mengalami perubahan secara volume maupun tekananya. Secara sederhana prinsip kerja mesin diesel dalam PLTD dapat dijelaskan sebagai berikut; perta bahan bakar dalam tanki bahan bakar misal MFO, HSD mapun B30 yang dialirkan dari daily tank dipompakan kedalam nozzle yang berfungsi sebagai pengabut yang menerima injeksi bahan bakar bertekanan tinggi dan temperature juga naik seiring kenaikan tekanan fluida. Supplai udara kedalam diesel dialirkan dari tanki udara melalui air intake system kemudian dialirkan melalui turbocharger untuk lebih mengefisiensikan dengan meningkatkan tekanan udara yang masuk. Turbocharger sendiri bekerja seperti mesin kompresi sentrifugal yang mendapat daya turbinnya dari gas buang. Tekanan yang dicapai udara mencapai 500 psi (34 bar) dan temperature 600 degC kemudian dialirkan ke ruang bakar secara simultan dengan aliran bahan bakar. Udara bertekanan dan temperatur tinggi yang masuk dalam silinder di ruang bakar akan membantu terjadinya self ignition dari bahan bakar ketika disemprotkan sehingga terjadi “ledakan” sehingga dapat menggerakkan torak yang dihubungkan dengan poros engkol oleh batang penggerak dan menyebabkan pergerakan secara rotasi poros rotor (generator) dan dikonversikan menjadi energi listrik.
Mesin diesel menggunakan prinsip reciprocating memiliki komponen utama yang berperan dalam mekanisme konversi energi seperti pada gambar berikut;
Sunday, August 7, 2022
Numerical Study Of Gas Mixing Effect On Block 3 & 4 Muara Tawar’s Gas Turbine Combustion Stability
DOI: 10.1007/978-981-19-1581-9_33
Abstract. Gas turbine operation’s disturbances related to combustion that lead to flame instability greatly influenced by the setting of fuel and air which is adjusted according to gas availability during commissioning. Meanwhile, gas turbine must be able to operate using a variety of natural gases or its mixing depending on the system and gas availability. This study presents the numerical simulation to obtain the combustor’s characteristics by analysis the flame stabilization, temperature distribution, and Nox emission by varying the fuel gas sourced and air mass flow. The numerical analysis has shown that fuel with higher CH4 contains will tend the ombustion become more unstableand and stabilized by the inner recirculation zone. The more excess air also provide more stable combustion as flame lenght decrease, but too much excess air will decrease the total temperature. NOx emission produced from the combustion which produce higher temperature from methane and excess air effect. The recommendation of the research results is to provide a limitation of the composition of the gas mixing and the fuel air ration to obtain the combustion stability. The results of the study simulate that it is possible to use three condition of fuel gas in combustion system.
air.
1. Introduction
istics and highlights the benefits of using fuels with higher hydrogen–carbon ratios including higher
power, higher efficiency, and lower carbon emissions. Author [3] the investigation to analyze the V94.2
gas turbine’s fluid flow and heat transfer on burner performance.
Based on these previous studies, the research is carried out by evaluating and optimizing the
combustion characteristics and temperature distribution by varying the fuel gas sourced and provide a
limitation of the composition of the gas mixing and the ratio of air to fuel (air fuel ratio) to obtain the
combustion stability.
2. Methods
Prior to the combustion simulation in the burner, the geometry is made to check whether it is close
to the actual condition based on the parameters in the gas turbine operating parameters. The geometry
(figure 1) test is done by simulating the fuel inlet, air inlet and combustion chamber outlet in one of the
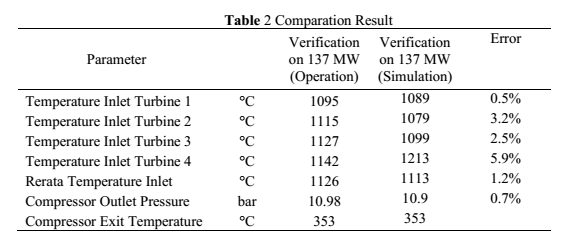
operating conditions based on the composition of the gas used then the parameter results, especially
several points of turbine inlet temperature and turbine inlet pressure, are compared with operating
parameters as seen on table 1.
operation condition. Methane is a fuel gas contain that used as the reference of this analysis. Since the
actual composition during operating of the Muara Tawar’s gas turbine couldn’t accurately calculate (no
gas chromatograph to sense mixing gas) there were three gas classification, high composition (CH4
94%), medium (CH4 87%) and low (CH4 71%).
3.1 Flame Stability
The flame length is one of the stability parameters combustion mechanism which closely related to
the mixing of fuel and air. The increasing of flame length indicated the combustion happened away from
the burner tip and tend to flame becomes unstable. The combustor design that applied the air swirl help
to increase the combustion intensity and reduce the flame length. Swirl flow also provided an angular
velocity to the axial incoming flow to produce a central recirculation zone (CRZ) which provides the
main flame stabilization.
longest flame length arround 4.7 m from burner tip. Amer and Gad [4] studied experimentally the effect of increasing air to fuel ratio on experimental study of LPG combustion. Increasing the air to fuel mass
ratio (excess air) from 5% to 20%, the flame length decreases by about 6% to 16%. The flame length
that indicated the lift will be stabilized by inner recirculation zone.
Recirculation zone on figure 2 showed the negative axial velocity in the center of the combustion
chamber indicates the presence of an inner recirculation zone due to circulating air flow made by swirl
air inlet which results in a vortex breakdown process and initiates a recirculation zone in the center of
the combustion chamber. The composition of the fuel with a higher methane content results in a wider
circulation zone when compared to fuel with a lower methane content as seen on figure 2. The length of
recirculation about 3.4 m and for low methane reached 2.1 m. The result of analysis clearly explain on
figure 3 that calculate on each gas composition and excess air.
The addition of excess air changes the characteristics of the recirculation zone, the more excess air
resulting in shorter recirculation center distances with a larger recirculation zone area. Hong, et al [5]
made some study on recirculation zone as excess air raised. The higher temperature of the products
reduces the velocity gradient in the shear layer and thus the reattachment length. The addition of 5%
excess air reaching 504 kg/s resulted in a recirculation center distance of 2.38 m from the burner tip.
3.2 Temperature Distribution
Combustion process is a reaction between fuel gas and oxygen in the air. The result of this process
were carbon dioxide (CO2), water (H2O), and a great deal of energy. The higher methane content, the
higher the maximum temperature reached. The length of maximun temperature also increases from the
tip burner. The addition of excess air as showed on figure 4 shows that as the amount of air increases,
the temperature to the outlet will decrease this is due to the combustion losing a certain amount of energy
because too much air enters the combustion chamber.
The addition of excess air from 15% to 20% does not cause a significant increase in maximum
temperature and energy. The combustion efficiency increases with increased excess air until the heat
loss in the excess air is larger than the heat from combustion. Munir et al [6] evaluate the effect of excess
air on combustion concluded that an optimum air fuel ratio should be maintained to ensure complete
combustion as well as to decrease the excessive losses due to surplus air.
3.3 NOx Emission Characteristic
Nox emission is produced by the oxidation of atmospheric nitrogen in high temperature regions of
the combution flame and postflame gases at the outlet. Previously reported sitgnificant effects on NOx
characteristic by Thomson, et al [6] that the nitric oxide formation rate in post flame gases of
hydrocarbon flames (T > 1800°K) and follows the Zeldovich chain mechanism. The combustion process
will lead the creation of nitrogen oxides from nitrogen from air or gas fuel. At higher temperatures both
can react to form NOx in large quantities. The formation of the NOx mass fraction in combustion with
variations in the methane content shows a higher value due to ethane increasesing as shown in figure 5.
The addition ofexcess air in combustion will also affect the reaction of NOx mass fraction as a result
of combustion temperatures that becone lower. This is the point that the excess air become too much.
as excess air.
4. Conclusion
The analyses were carried out for combustion characteristic for gas turbine type V94.2 using several
composition of natural gas that being used as fuel in Muara Tawar power plant. Through the numerical
simulations it was possible to notice that:
• The more flame lenght on Fuel with a greater methane content results the flame lenght increasing
and tend to unstable combustion.
• The CRZ distance is about 3.4 m and with a methane content of 94% and the more excess air will
lead the CRZ becomes shorter but the area of recirculation become wider.
• The addition of excess air causes the temperature to decrease at the outlet area of the combustion
chamber due to combustion losing some energy because too much air enters the combustion chamber.
• Temperature plays an important role in the formation of the mass fraction of NOx, the lower the
temperature the less mass fraction of NOx is produced.
• The addition of excess air of about 5% provides the most optimal combustion stability and emission
factor values.
• The results of the analysis clearly demonstrate that it is possible to use such fuels in combustion
systems with swirl burners.
Friday, May 13, 2022
Carbon Capture & Storage
Carbondioxide Capture and Storane (CCS) merupakan salah satu mitigasi adanya pemanasan global dengan cara mengurangi emisi CO2. Teknologi CCS merupakan rangkaian pelaksanaan proses yang terkait satu sama lain, mulai dari pemisahan dan penangkapan (capture) CO2 dari sumber emisi gas buang (flue gas), pengangkutan CO2 yang tertangkap ke tempat penyimpanan (transportation), dan penyimpanan ke tempat yang aman (storage).
Tabel 2. Emisi dari sector pembangkit energi
- Mengurangi konsumsi energi bahan bakar, contohnya dengan meningkatkan efisiensi dari konversi energi.
- Beralih penggunaan bahan bakar dengan kandungan karbon yang lebih rendah, seperti penggunaan gas dibanding batu bara.
- Peningkatan penggunaan energi terbarukan atau energi nuklir yang menghasilkan emisi CO2 yang rendah atau tanpa emisi sekali.
- Penangkapan gas CO2 secara biologi atau secara alami dengan meningkatkan kemampuan hutan dalam penyerapan CO2.
- Teknologi menangkap dan menyimpan CO2 secara kimiawi dan metode fisis.
- Menangkap CO2 dari proses industry, salah satunya dikenal dengan metode sweetening yaitu mengurangi kandungan CO2 dalam gas alam.
- Teknik post-combustion, menangkap CO2 dari gas buang pembangkit listrik setelah bahan bakar fosil dibakar. Gas buang akan melewati absorber tower yang mempunyai bahan kimia khusus (biasanya amina). Amina berfungsi untuk menyerap CO2 dari gas buang
- Teknik pre-combustion biasanya diterapkan pada Integrated Gasification Combine Cycle (IGCC) yaitu pembangkit listrik tenaga batu bara dan penangkapan CO2 dilakukan sebelum batu bara benar- benar membara. Batu bara dipanaskan secara perlahan untuk mengeluarkan synthetic gas yang terdiri dari karbon monoksida dan hydrogen.
- Teknik oxyfuel combustion yaitu membakar bahan bakar fosil dengan oksigen murni alih-alih dengan udara. Gas buang yang dihasilkan hampir seluruhnya terdiri dari CO2 dan air. Air dikeluarkan melalui kondensasi sedangkan CO2 dikompresi agar dapat dipindahkan. Tehnik ini dapat menghasilkan tingkat penangkapan CO2 yang sangat tinggi, kekurangannya metode ini membutuhkan banyak energy untuk menghasilkan oksigen murni sehingga relative tidak efisien.